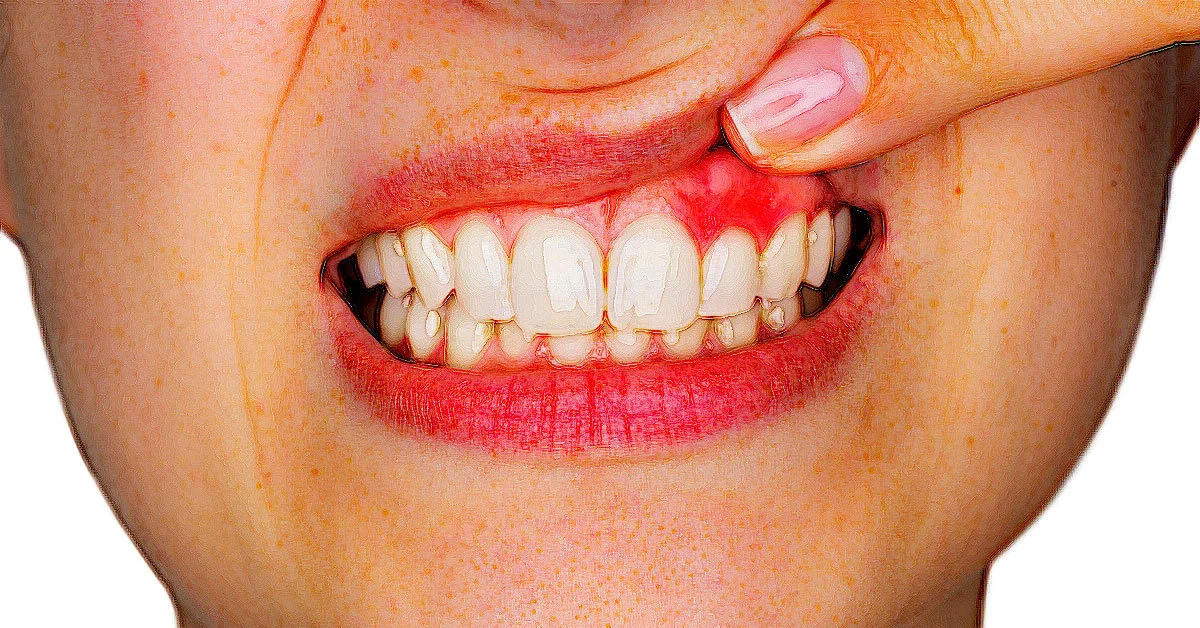
Gum disease and tooth sensitivity are two common dental issues affecting millions of people. Often linked, these conditions can significantly impact your oral health. If you’ve ever experienced bleeding gums or a sharp, sudden pain while drinking something hot or cold, it might be time to seek bleeding gum treatment in Panvel and explore how gum disease may be contributing to your discomfort. By understanding the relationship between these two issues, you can take proactive steps to protect your oral health.
In this blog, we’ll explore the connection between gum disease and tooth sensitivity, how each condition develops, and what you can do to prevent and manage them effectively.
Understanding Gum Disease
Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is an infection of the tissues surrounding and supporting your teeth. The early stage of gum disease is called gingivitis, which is characterized by bleeding, swelling, and redness of the gums. If left untreated, it can progress to periodontitis, a more severe condition that affects the tissues and bones holding your teeth in place. In advanced cases, periodontitis can lead to tooth loss.
Gum disease is primarily caused by plaque, a sticky film of bacteria that forms on your teeth. Without regular brushing and flossing, plaque hardens into tartar, irritating the gums and leading to inflammation.
Common Symptoms of Gum Disease:
- Red, swollen, or tender gums
- Bleeding gums, especially during brushing or flossing
- Receding gums (gums pulling away from the teeth)
- Persistent bad breath (halitosis)
- Loose or shifting teeth
Tooth Sensitivity: What It Is and Why It Happens
Tooth sensitivity is characterized by sharp, sudden pain when your teeth come into contact with hot, cold, sweet, or acidic foods and drinks. This occurs when the protective enamel layer on your teeth becomes worn down, exposing the underlying dentin. Dentin contains tiny tubules that connect to the tooth’s nerves, and when exposed, they can cause pain when triggered by external stimuli.
Causes of Tooth Sensitivity:
- Gum Recession: As gums recede, the roots of the teeth become exposed. Since the roots don’t have a protective enamel layer, they are highly sensitive to temperature changes and other stimuli.
- Enamel Erosion: Brushing too aggressively or consuming acidic foods can wear down enamel, leading to sensitivity.
- Tooth Decay: Cavities and worn fillings can also expose dentin and lead to sensitivity.
How Gum Disease and Tooth Sensitivity Are Connected
The connection between gum disease and tooth sensitivity lies in gum recession. As gum disease progresses, the gums pull away from the teeth, exposing the roots. These exposed roots, which lack enamel, become sensitive to hot, cold, and acidic foods and drinks. Therefore, tooth sensitivity is often a symptom of advanced gum disease.
Additionally, the inflammation caused by gum disease can worsen the condition by creating pockets between the gums and teeth. Plaque and bacteria accumulate in these pockets, exacerbating gum recession and increasing sensitivity.
Preventing Gum Disease and Tooth Sensitivity
Both gum disease and tooth sensitivity are preventable with good oral hygiene and a few lifestyle adjustments.
- Brush and Floss Regularly: Brushing twice a day and flossing daily is essential for preventing plaque buildup, which leads to gum disease. Use a soft-bristled toothbrush and gentle strokes to protect your gums and enamel.
- Use a Desensitizing Toothpaste: Toothpastes designed for sensitive teeth can block pain signals from the tooth surface to the nerve.
- Rinse with Mouthwash: An antibacterial mouthwash can help reduce plaque and prevent gum disease. Choose alcohol-free options to avoid dry mouth.
- Watch Your Diet: Limit acidic foods and drinks like soda, citrus, and wine, as they can erode enamel and worsen sensitivity.
- Visit Your Dentist Regularly: Regular check-ups are vital for early detection of gum disease and tooth sensitivity. Your dentist can recommend treatments such as fluoride varnishes or sealants to protect your teeth.
- Avoid Aggressive Brushing: Brushing too hard can wear down enamel and damage gums. Use gentle pressure with a soft toothbrush.
Treating Gum Disease and Tooth Sensitivity
If you already have gum disease or tooth sensitivity, treatments are available to manage these conditions and restore your oral health.
- Scaling and Root Planing: For gum disease, your dentist may recommend this deep cleaning procedure to remove plaque and tartar from below the gumline, allowing the gums to reattach to the teeth.
- Desensitizing Treatments: In-office treatments like fluoride gels or bonding agents can protect exposed dentin and reduce sensitivity.
- Gum Grafting: In cases of severe gum recession, your dentist might suggest gum grafting, where tissue from another part of your mouth is used to cover exposed roots and reduce sensitivity.
- Periodontal Therapy: For advanced gum disease, more intensive treatments or surgery may be required to remove bacteria and stabilize the teeth.
Conclusion
Gum disease and tooth sensitivity can significantly impact your oral health, but with proper care and early intervention, both conditions are preventable and manageable. By maintaining a good oral hygiene routine, using products for sensitive teeth, and visiting your dentist regularly, you can keep your gums healthy and protect your teeth from sensitivity.
If you’re experiencing bleeding gums or sensitivity, seek professional advice for bleeding gum treatment in Panvel. Taking care of your gums now can prevent discomfort and ensure a healthy smile for years to come.